
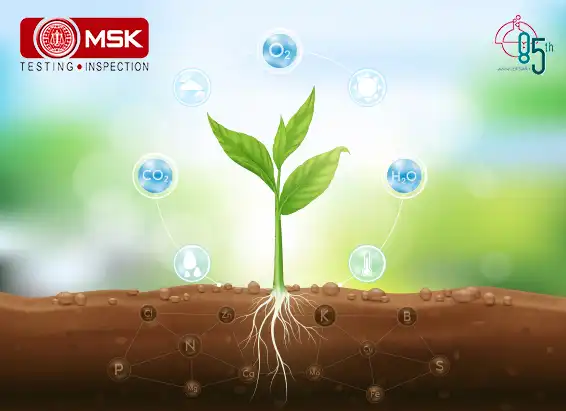
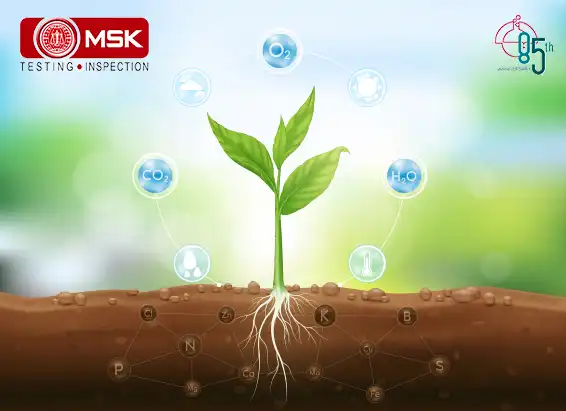
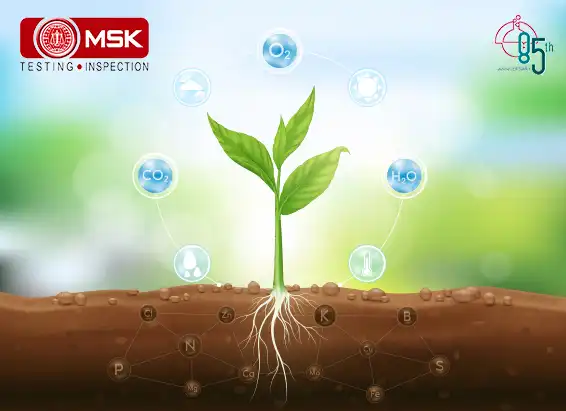
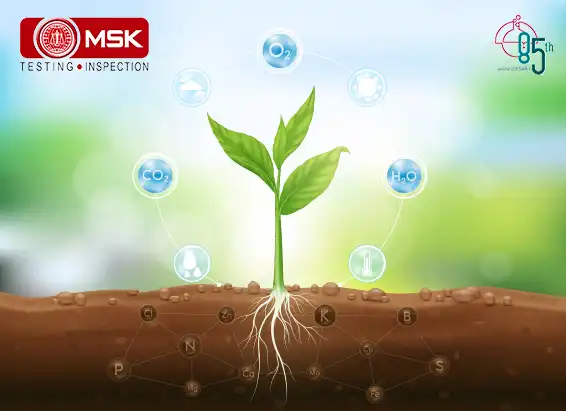
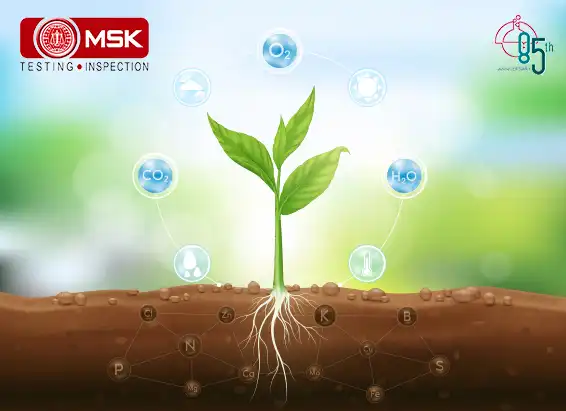
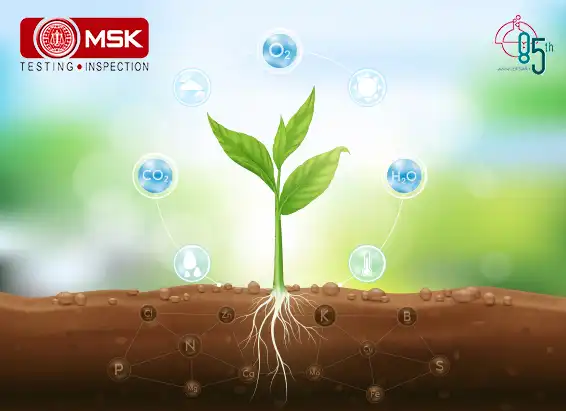
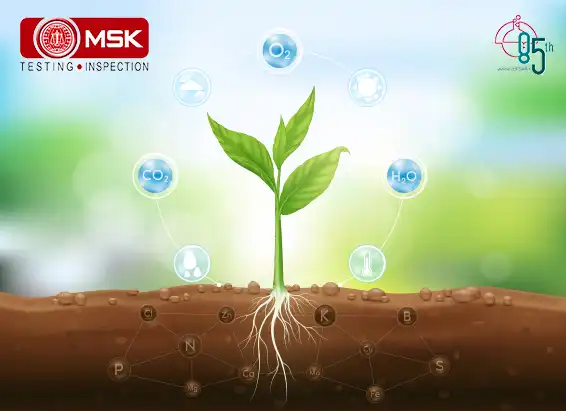
GHGs directly trap heat and increase global warming but there is another concept that is becoming alarmingly serious, the indirect GHGs which do not trap heat themselves but contribute to global warming through their own chemical transformations, influencing the atmospheric lifetime of other greenhouse gases, and affecting the absorptive characteristics of the atmosphere such as affecting cloud formation (United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Inventory” ES-2). Some are grouped as follows
Nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon monoxide (CO) react in the atmosphere, forming tropospheric ozone.
Explanation is as follows. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) act as indirect greenhouse gases by producing the tropospheric greenhouse gas 'ozone' via photochemical reactions in the atmosphere. Like tropospheric ozone, NOx gases also affect the global greenhouse gas budget through their effect on the atmospheric abundance of hydroxyl (OH) radicals (Satein,2009). However there is an opposite role also played by this entity. The breakdown of NOx gases gives rise to increased OH abundance and so helps to reduce the lifetimes of greenhouse gases like methane (http://www.ghgonline.org/othernox.htm). Sources of NOx include fossil fuel burning, biomass burning and emission from soils.
Methane and other gaseous organic compounds are collectively known as Volatile Organic Compounds, or VOCs. In greenhouse gas assessments, methane is addressed separately, as it is the most significant VOC, and VOCs refer to the other compounds. The abbreviation NMVOC (Non-Methane Volatile Organic Compounds) is also commonly used.
VOCs have a direct effect by absorbing heat radiation from the ground, but their indirect contribution is more significant. They react with hydroxyl radicals (OH-) in the air, forming tropospheric ozone, which is a greenhouse gas. When they reach the stratosphere, they react with OH-, forming water vapour, which is a greenhouse gas. VOCs are also converted to methane. (https://www.genano.com/infobase/greenhouse-gases-and-their-harmful-effects)
Hydrogen is considered an indirect greenhouse gas because, it interacts with airborne molecules called hydroxyl radicals to prolong the lifetime of atmospheric methane — a highly potent greenhouse gas — and increase the production of ozone, another greenhouse gas.
Hence we must monitor these Indirect GHGs to account for the total Global Warming Potential. Detection of such gases must be made mandatory along with the routine parameters so that better mitigation measures can be taken.
MSK SCOPE
MSK monitors indirect indirect GHGs as follows:
By monitoring these gases, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of their impact on global warming and implement effective strategies to mitigate their emissions.
Compiled by Dr. Chitralekha Sengupta
Contributed by Mitra S.K. Environmental Testing Services (Division) and Mitra S.K. Laboratory Services


Chief Operation, FAMD, Tata Steel Limited..


Sr. General Manager,, Emirates Trading Agency L.L.C..


Mines Manager, Hindustan Zinc Limited, a Vedanta Company.


General Manager, Stevin Rock L.L.C..


Executive Vice President (Works),, DCW Limited.


AVP – Coal Quality & Sales Compliance Head,, PT Indo Tambangraya Megah Tbk (BANPU).


Laboratory Head, MMX.


Shipping Administrator, Mount Gibson Iron Limited.


Senior Director – Asia Pacific Iron Ore Sales,, Cliffs Natural Resources Pty Ltd..


Member, Compass Group (India) Pvt. Ltd.

Posted on January 16 2026 By Mitra S.K ADMIN
Read More
Posted on January 16 2026 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on January 16 2026 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on January 16 2026 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on January 16 2026 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 16 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 16 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 16 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 11 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN
![Estimating Cobalt by UV-Vis Spectroscopy: The [CoCl?]²? Acetone Method](https://mitrask.com/uploads/blogs/1764834098Estimating%20Cobalt.png)
Posted on December 04 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN
Posted on December 04 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on November 12 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on September 23 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on August 01 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on July 25 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on July 18 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on July 01 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on May 22 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on January 24 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on January 24 2025 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 31 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 31 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN
Posted on December 31 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 31 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 31 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 03 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on October 17 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on October 04 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on September 13 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on August 27 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on August 23 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on June 27 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on June 22 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on June 15 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on May 24 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN
Posted on May 17 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on May 09 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 20 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 13 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 30 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 29 2024 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 30 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 30 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 30 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 27 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on December 26 2023 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 05 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on November 28 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on April 06 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on November 28 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN

Posted on June 14 2022 By Mitra S.K ADMIN






